Oocyte quality
Oocyte quality is a key limiting factor in female fertility
- Oocyte is not passive in the ovarian follicle
- Oocyte plays a central role in the regulation of folliculogenesis and thereby its own development
There is no accurate test for measuring egg quality
- A mature oocyte to be fertilised and develop to an embryo
- Quality of the originating gametes is of utmost importance in the development of the embryo
- The only reliable measurement of oocyte quality is whether fertilization and embryologic development leads to a normal baby
Oocyte quality evaluation
- Morphological
- Clinical
- Cellular and Molecular
- Biochemical
- Genetics
Morphological evaluation
- Cumulus–oocyte complex
- Oocyte cytoplasm
- Oocyte size
- Polar body
- Perivitelline space
- Zona pellucida
- Meiotic spindle
Oocyte quality evaluation
Clinical measurement of oocyte quality
Perifollicular vascularization evaluation
Insufficient perifollicular vascularization measured using color Dopler USG is suggested to correlate with intrafollicular hypoxia, inducing oocyte cytoplasmic defects, disorganised chromosomes, reduced fertilization and embryos with multinucleated blastomeres
–Not easy to assess
–Association not confirmed by some studies
Van Blerkom J, 1996
Van Blerkom J et al. 1997
Battaglia C et al. 2000
Oocyte quality evaluation
Cellular
The oocyte is a central regulator of follicular cell function and plays a critical role in the regulation of oogenesis, ovulation rate and fecundity
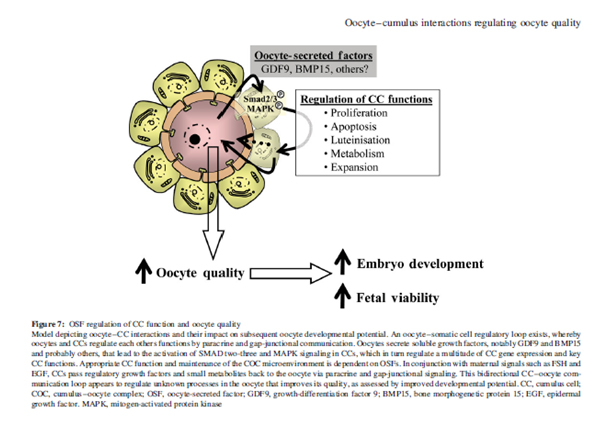
Oocyte-cumulus interactions regulating oocyte quality
- CC-oocyte gap-junctional signalling
- CC-oocyte bidirectional paracrine signalling
Molecular
Oocyte secreted factors (OSF)
- Growth differentiation factor 9 (GDF-9)
- Bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP-15)
– Absence of these two oocyte-spesific growth factors causes sterility
Biochemical predictors of oocyte quality
Hormones (in follicular fluid)
- Gonadotropins
- Growth hormone
- Prolactin
- Estrogens, progesterone and androgens
- Corticoids
- Metabolomics of follicular fluid
- Follicular AMH measurement
Genetic diagnosis on oocyte
PGD of first polar body
Gene expression in cumulus cells
Proteomic profiles generated from single oocytes
Impacts on oocyte quality
- Age
- Ovarian reserve
- Stimulation
- High E2 level
- PCOS
- Culture conditions
- chemotherapy/radiation
- certain genetic conditions
- ……
At this time, the best test of egg quality is female age

Stimulation & medication & oocyte quality
- Gonadotrophin dose, type
- Duration of stimulation
- Coasting
- Timing and duration of use of GnRH antagonist
- Transdermal testosterone gel
- Myo-inositol
- Melatonin
- Growth hormone
- Metfomin
- Oral contraceptive pill pretreatment
- LH suplementation
- Flushing
COS
- Higher total gonadotrophin dose adversely affect clinical pregnancy in normo-responder patients undergoing ICSI cycles with long protocol
Yılmaz N et al. ArchGynecolObstet. 2013
Correlation between euploidy and stimulation protocol
- Moderate Ovarian Stimulation Does Not Increase the Incidence of Human Embryo Chromosomal Abnormalities in in Vitro Fertilization Cycles
Labarta E et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012
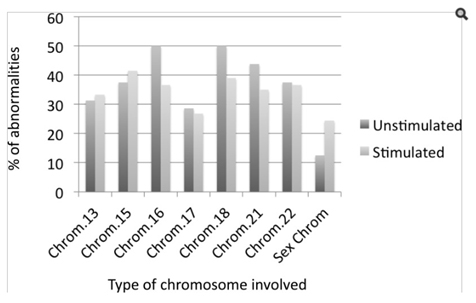
Conclusions: Moderate ovarian stimulation in young normo‐ovulatory women does not significantly increase the embryo aneuploidies rate in in‐vitro fertilization derived human embryos as compared with an unstimulated cycle.
- Recent findings suggest that the magnitude of ovarian stimulation affects the proportion of euploid embryos
- Numerical chromosomal abnormalities (aneuploidy) are present even in embryos of young women, and in the absence of ovarian stimulation
- Both studies is limited by the fact that 9chr FISH is an unappropriate strategy to perform PGS
- Blastomere stage is subjected to a number of problems among which mosaicism is the most critical.
- These results could then be misleading and the analysis might be better reconducted at the blastocyst stage through 24chr platforms (aCGH)
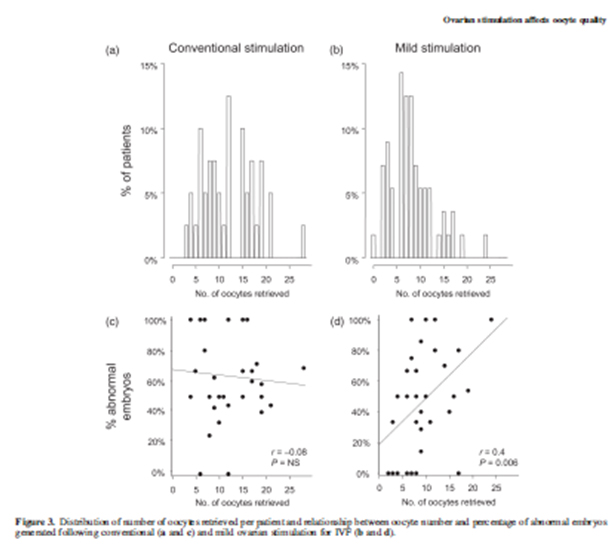
Mild stimulation
- Milder ovarian stimulation for in-vitro fertilization reduces aneuploidy in the human preimplantation embryo
Baart EB, Hum Rep 2007
- Future ovarian stimulation strategies should avoid maximizing oocyte yield, but aim at generating a sufficient number of chromosomally normal embryos by reduced interference with ovarian physiology
Duration of gonadotropin
- Fewer number of oocytes in short antagonist protocol
- It may not affect the outcome of IVF-ET
Huang S. 2013
Coasting
- Coasting seems to be associated with a reduced oocyte collection rate, especially when the coasting period is prolonged.
- However, this does not result in reduced oocyte quality. The length of the coasting period and degree of estradiol decrease do not seem to alter the results in terms of pregnancy rates.
Delvigne A 2003
- Short coasting of 1 or 2 days by withholding both gonadotropins and gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist prevents ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome without compromising the outcome.
Moon HS 2008, Nardo LG 2006, Gafar AH 2002
Timing and duration of use of GnRH antagonist
- GnRH-antagonist duration of use or starting day did not influence oocyte quality, implantation rates, and pregnancy rates
Detti L 2008
Impact of GnRH analogues on oocyte/embryo quality (vs antagonist)
- The rate of cytoplasmic abnormalities in retrieved oocytes was significantly higher with the use of GnRH antagonist than in GnRH agonist cycles
- lower rate of zygotes showing normal pronuclear morphology and higher cell-number of preembryos on day 2 after fertilization with the use of GnRH antagonist
Clinical pregnancy rate per embryo transfer was same
Murber A et al. 2009
Urinary-FSH vs rec-FSH
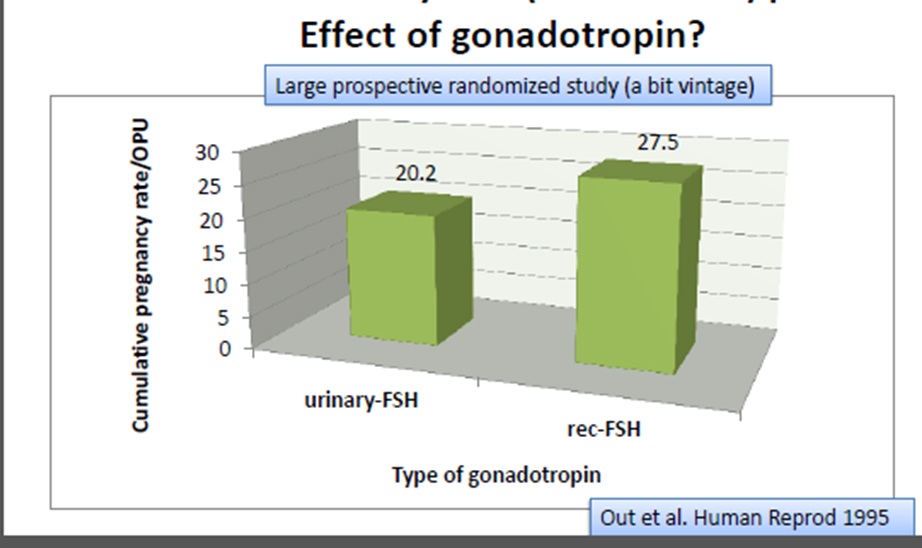
Recombinant versus human derived follicle stimulating hormone
- No significant difference in oocyte/embryo quality was observed between the two groups
- hFSH and rFSH products are equivalent in terms of clinical efficacy
Abate A. Et.al. 2009
van Wely M 2011 Cochrane Database SystRev
Murber A. 2011
Human derived and recombinant follicle-stimulating hormone for ovarian stimulation
- The combination of human and recombinant FSH for ovarian stimulation may produce a positive effect on follicular development as it improve oocyte quality, embryo development, and ultimately clinical outcome in RIF
Selman H et al., EurRevMedPharmacolSci. 2013
hMG & yield of mature oocytes
- In a selected group of patients with >20% oocyte immaturity during an IVF cycle with FSH alone, the addition of hMG to the stimulation protocol results in a higher yield of mature oocytes and excellent-quality embryos
Huddleston HG et all. 2009
Oral contraceptive pill pretreatment vs GnRH agonist protocol in PCO
- Clinical and ongoing pregnancy rates were significantly lower in the OCP group despite same oocyte and embryo quality
- The cumulative pregnancy rate did not differ between the two groups
- Extended duration of OCP pretreatment, as a first intention IVF protocol for PCO patients, does not improve the pattern of follicular growth nor the oocyte and embryo quality
Decanter et all. 2013
LH suplementation
- A beneficial effect when small doses of LH are used for ovarian stimulation in IVF-ET cycles
- Statistically significantly better in terms of the number of mature oocytes, the number of fertilized oocytes as well as the number of transferable embryos
- This effect may be more important in cases in which few embryos are available for transfer.
- Clinical pregnancy rate, finally, was similar in the two groups
Drakakis P et al. Eur J ObstetGynecolReprodBiol. 2005
LH suplementation
- Adding hCG to rFSH in COS for IVF from the start of stimulation resulted in a significant increase in the number of top quality embryos per patient
- There were no improved pregnancy rates with rLH supplementation
Mochtar et al., 2007 Cochrane review
- No significant difference in embryo quality after the addition of rLH to rFSH for ovarian stimulation in women with poor ovarian reserve
Musters AM et al. Hum Reprod. 2012
Oocyte quality & severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- Oocyte quality is not compromised in severe OHSS cycles irrespective of whether patients had or did not have PCOS
- Oocyte and embryo yield and quality were similar in early and late OHSS
- Oocyte yield and quality, embryological outcome, and implantation and pregnancy rates were similar in patients with and without polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) both in cycles developing OHSS and control cycles.
Fabreques F et al. Fertil Steril. 2004
Influence of ratios of oestradiol
- The E2/fol levels correlated positively with NRO (retrieved)
- negative correlations between E2/o and NMO
- Oocyte quality scores were not affected from either E2/fol or E2/o levels
- high E2/fol ratio may have beneficial effects on NRO, NMO and NFO while E2/o may adversely affect these parameters
Ozdeğirmenci O,2011
Relationship between number of oocytes retrieved and ongoing pregnancy rate
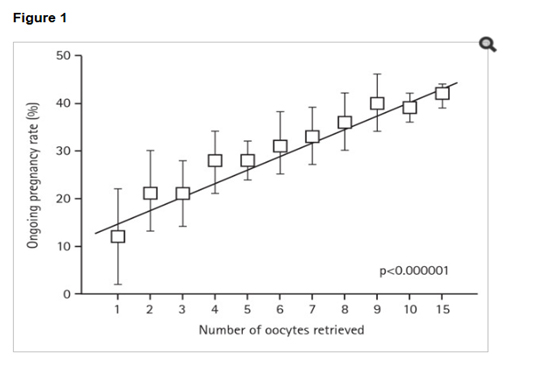
Bosch E, Ezcurra D. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011
Ongoing pregnancy rate according to ovarian response in an unselected population (source: Instituto Valenciano de Infertilidad, between 2004 and 2008, n = 7954, p < 0.000001 [Mantel-Hansen test for trend]).
transdermal testosterone gel
- The numbers of oocytes retrieved, mature oocytes, fertilized oocytes, and good-quality embryos were significantly higher in the TTG pretreatment group.
- Embryo implantation rate and clinical pregnancy rate per cycle initiated also were significantly higher in the women pretreated with TTG.
- TTG pretreatment might be beneficial in improving both response to COS and IVF outcome in low responders undergoing IVF/ICSI
Kim CH 2011, Sunkara SK 2011
- Transdermal testosterone prior to ovarian stimulation significantly increases live birth and reduces the doses of FSH required among poor responders
- No differences were observed in the number and quality of the oocytes retrieved
- the identification of poor responders that could especially benefit from testosterone treatment should be addressed in further studies.
Gonzales CM 2012
Myo-inositol
(An isomer of C6 sugar alcohol that belong to the vitamin B complex group )
- The average number of immature oocytes was significantly reduced (vesicles germ and degenerated oocytes) too.
- The supplementation of inositol, due to its ability to increase insulin sensitivity, improves the oocytes’ quality and increase the number of oocytes collected after ovarian stimulation in patients undergoing IVF (In Vitro Fertilization
Ciotta L. Et. Al. 2010
- Myo–inositol may be useful in the treatment of PCOS patients undergoing ovulation induction, both for its insulin-sensitizing activity, and its role in oocyte maturation
Ciotta L. Et. Al. 2011, Gerli S 2007, Unfer V. 2012, Nesler JE 2000
Melatonin
- Oxidative stress impairs oocyte quality and melatonin protects oocytes from free radical damage and improves fertilization rate.
- Melatonin is likely to improve oocyte quality and fertilization rates
Tamura H 2008, Batıoğlu AS 2012, Rizzo P 2010
Myo-inositol plus folic acid plus melatonin
- melatonin ameliorates the activity of myo-inositol and folic acid by improving oocyte quality and pregnancy outcome in women with low oocyte quality history
Rizzo P et al. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010
- High maturation rate
- Fertilization rate did not differ
- Clinical pregnancy rate and implantation rate were in tendency higher in the group cotreated with melatonin, although the differences did not reach statistical significance
- Biochemical pregnancy rate and abortion rate were similar

- The treatment with myo-inositol and melatonin improves ovarian stimulation protocols and pregnancy outcomes in infertile women with poor oocyte quality
- Higher concentrations of MI and E2 in human FF appear to play a role in follicular maturity and provide a marker of good quality oocytes
Chiu TTY et al. Hum. Rep. 2002
Growth hormone
- Addition of growth hormone (GH) during ovarian stimulation in patients with poor-quality oocytes increased the pregnancy rate
- Beneficial in RIF patients
- An improvement of cytoplasmic competence is proposed as an explanation
Hazout A, 2009
Metformin
- Pre-treatment with metformin prior to conventional IVF/ICSI in women with PCOS does not improve stimulation or clinical outcome.
- However, among normal weight PCOS women, pre-treatment with metformin tends to improve pregnancy rates.
- Further studies in subgroups of PCOS women are required.
Kiotrod SB 2004
Follicular diameters and flushing
- Follicles larger than 18 mm at retrieval have consistently mature oocytes with a higher rate of fertilization
- Small size follicles are still capable of containing mature oocytes, but their rate of abnormal or no fertilization is high (12-18 mm)
- Oocytes recovered with flushing are still able to produce embryos with full developmental competence.
Mehri S et. al. 2014

- Follicular flushing in the poorest responders does not increase the number of oocytes retrieved and may result in lower implantation and clinical pregnancy rates.
Vaginal disinfection
- No differences in the fertilization & cleavage rates and PR were found in the betadine & normal saline groups (van Os et al,1992).
- However CPR was significantly higher in the normal saline group (17.2% Vs 30.3%).
- No increase in infections in saline group
- There is no indication to used iodine,
Methotrexate administration for ectopic pregnancy after IVF
- Methotrexate does not compromise ovarian reserve, ovarian responsiveness, or IVF success in subsequent cycles
Boots CE et al. 2013
Efficacy of in vitro fertilization after chemotherapy
- The efficacy of IVF is dramatically reduced after even one round of chemotherapy
- IVF should be performed before chemotherapy
- For those who require immediate chemotherapy, ovarian tissue cryopreservation and/or oocyte cryopreservation could be used before treatment
Dolmans MM et al. Fertil Steril. 2005
smoking
- Cigarette smoking increases the zona pellucida thickness of oocytes and decreases a quality of oocytes
Depa-Martynow M et. al. 2006
Shiloh H et al 2004
Krizanowska K 2002
- The fertilization rate of oocytes and the pregnancy rate were not significantly different between smokers and nonsmokers
- Significantly alterated hormonal parameters and negatively influenced oocyte parameters, particularly after clomiphene stimulation.
Weigert M, 1999
Conclusion-1
- Morphological evaluation of oocyte quality may be subjective and controversial, it still can provide valuable information, and is practical, convenient in daily work
- The only reliable measurement of oocyte quality is whether fertilisation and embryologic development lead to a normal baby
Conclusion-2
- Several studies seem to show that ovarian stimulation has an influence on oocyte quality, especially at a chromosomic and perhaps, epigenetic level
- Magnitude of ovarian stimulation affects the proportion of euploid embryos
- Mild stimulation selects less oocytes but with better quality and produces euploid embryos
Conclusion-3
- GH, Melatonin and Myo-inositol may be useful in selected subgroup of patients
- Iodin is toxic to oocytes, cleaning with SF at OPU will protect oocytes from toxicity
