STEPS IN IVF
- Follicle suppression
- Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation
- Aspiration of eggs from follicles
- Fertilization, incubation and selection of embryos
- Embryo transfer
- Pregnancy test
Time of retrieval
- hCG can be administered at any time 34 to 38 hr before OR without affecting the results of IVF
(Bjerecke et al ,2000)
OPU Timing
- Exposure to high levels of LH before ovulation can have detrimental effects on the developing oocyte, (Even if ovulation did not occur)
- Earliest follicular rupture after hCG injection (termed surrogate LH surge) is about 39 hours and the latest is about 41 hours Andersen AG 1995, Taymor MI 1983
- Not all follicles rupture together and the largest is not necessarly the first to rupture
- Therefore OPU scheduled 36 hours after hCG injection
OPU
- This is usually performed in the morning or early afternoon, approximately 35-36 hours after the hCG injection
- Methods of egg collection
Laparotomy (first human pregnancy in IVF – 1973, Monash Un.
Laparoscopy ( Louise Brown – 1978, Steptoe and Edwards)
Abdominal ultrasound guided egg collection
Vaginal ultrasound guided egg collection
Transvaginal follicle puncture under sonographic control has become the method of choice for ovum retrieval worldwide.
Vaginal ultrasound guided egg collection
- The most common technique minor and safe surgical procedure usually performed under sedation or a general anesthetic. Sedation is a safe and ecceptable method of providing pain relief for egg collection.
- A vaginal ultrasound probe with a fine hollow needle attached to it, is inserted into the vagina.
- Under ultrasound guidance, the needle is then advanced from the vaginal wall into the ovary to suck out the fluid from
- the follicle which contains the egg. Each egg is removed in turn through the needle by a suction device.
- Follicle flushing is not associated with improvement in pregnancy rates or the number of eggs collected, but does increase the duration of the procedure and associated pains.
- The whole procedure takes about 20-30 minutes.
The aspirating needle
- Collection using smaller diameter needles had no significant effect on the number of oocytes collected per follicle aspirated, or on the subsequent fertilizing capacity of those oocytes (Aziz et al,1993).
- There was a significant reduction in pain perceived by the patient when the smaller needle was used during the collection.
Comparison of single- and double-lumen needles
- No differences between the two needles in the number of oocytes provided for IVF (Scott et al,1989).
- The double-lumen needle was more flexible and frequently deviated from the projected path as observed by ultrasound.
- The single-lumen needle may be preferable because it is technically easier to use.
- ≤4 folikül varsa DLN (Double lumen needle) flushing
- >4 folikül varsa SLN (Single lumen needle) without flushing
- Endometrioma veya hidrosalpenks yapılarına girilmişse profilaktik antibiyotik önerilir
Follicular flushing
- No significant difference in the number of oocytes retrieved, fertilization rate, PR. Significant shortening of operating time in the aspiration time in the aspiration only group
(Kinsland et al,1991)..
Follicular curettage
- Increases oocyte yield (13,9 vs 11,4)
Dahl et al. 2009
Avoiding turbulent flow (filling the tubing with fluid prior to aspiration to avoid non-laminar flow)
Vaginal disinfection
- No differences in the fertilization & cleavage rates and PR were found in the betadine & normal saline groups (van Os et al,1992).
- However CPR was significantly higher in the normal saline group (17.2% Vs 30.3%).
- No increase in infections in saine group
- There is no indication to used iodine,

Abdominal ultrasound guided egg collection
- Egg collection is performed by passing a needle through the abdominal wall into the ovaries under ultrasound guidance.
- This is usually performed if the ovaries are abnormally placed.
Laparoscopy
- Originally, eggs were always collected laparoscopically.
- This method of egg collection is hardly ever used nowadays, as it requires a general anesthetic, in addition to the risks of laparoscopy.
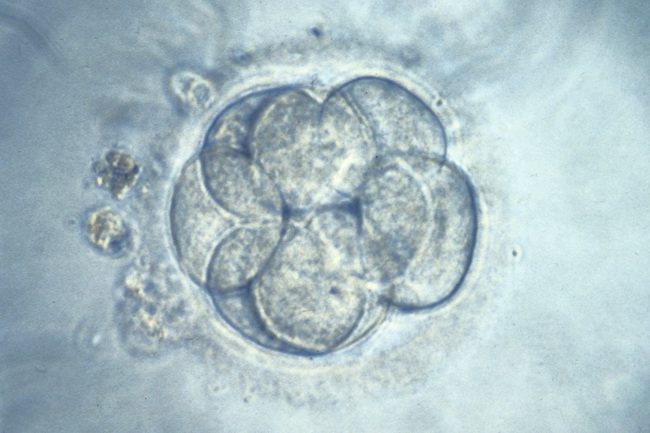
HIGH QUALITY EGG
COC
- Grade1: Kumulus yapısı yoğun hücre içeren radiyel bir şekilde genişlemiş ve homojendir.
- G2: Kumulus yapısı iyice genişlemiş, hücreler arası boşluklar yaygın ve gevşekçe kümeleşmeler izlenmektedir.
- MII oosit elde edilir.
1-COC:
- G3: Kumulus yapısı daha az genişlemiş ve cisimcik gibi görünen kümesel kumulus parçaları gözlenmektedir.
- G4: Kumulus yapısı oldukça yoğun ve kompakt izlenir.
- GV veya MI oosit.
- Ng et al.1999.
What happens after egg collection?
Complications
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Nausea and vomiting
- Trauma to pelvic srtructures
- Pelvic infection, tubo-ovarian or pelvic absccess
- Ovarian torsion
- Rupture of ovarian endometriosis
- Appendicitis
- Ureteral obstruction
- Vertebral osteomyelitis
- Anesthetic complications
- Empty follicle syndrome

Empty follicle syndrome
- Incidence is about 1%.
- Sometimes, giving another dose of hCG and scheduling another egg collection 24 hours later could salvage the cycle.
- The cause of empty follicle syndrome is unknown, but it is possible that it is a drug related rather than a clinical problem.
- Low bioavailability of hCG or poor bioactivity, inappropriate timing of hCG
- Rapid clearance of hCG by the liver
- Dysfunctional folliculogenesis (AMA)
Empty follicle syndrome
- Birkaç foliküle girildiği halde oosit gelmezse folikül sıvısında gebelik testi (İdrar kiti ile) veya kanda hCG bakılabilir.
- Gerekirse yeniden hCG verilip bir 36 saat daha beklenebilir
Administration of progesterone before OR
- Administration of 25 mg IM progesterone 12 hours before OR is associated with a lower PR than the administration of progesterone after OR (Sohn et al,1999).
- Vaginal progesterone started on the day of OR did not increase implantation or PR when compared to the same dose started on the day of ET (Baruffi et al ,2003) .
Administration of beta 2 adrenergic agonists on the day of OR
- Administration of 10 mg of terbutaline or 20 mg of ritodrine daily for 15 days starting on the day of OR was not associated with significant improvement in pregnancy, implantation or miscarriage rates
(Pinheiro et al,2003).
Definition
- Embryo transfer (ET): the procedure in which one or more embryos are placed in the uterus or Fallopian tube.
(ICMART)
Embryo transfer
- Quite simple and usually pain free
- The use of ultrasound scan during embryo transfer appears to increase pregnancy rates
- Transmyometrial ET (vary rarely)
Procedure
- Placing a speculum in the vagina to visualize the cervix, which is cleansed with saline solution or culture media.
- A transfer catheter is loaded with the embryos and handed to the clinician after confirmation of the patient’s identity.
- The catheter is inserted through the cervical canal and advanced into the uterine cavity, where the embryos are deposited.
- The catheter is then withdrawn and handed to the embryologist, who inspects it for retained embryos.
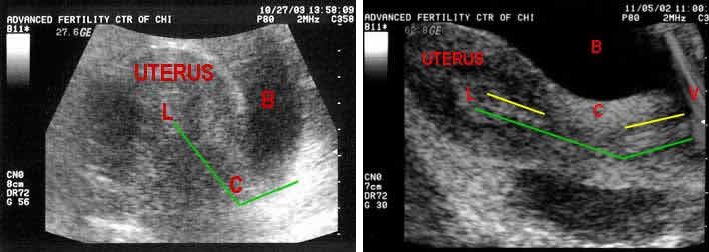
- An abdominal ultrasound is often used to ensure correct placement, which is 1–2 cm from the uterine fundus. Anesthesia is generally not required.
- Single embryo transfers in particular require accuracy and precision in placement within the uterine cavity. The optimal target for embryo placement, known as the maximal implantation potential (MIP) point, is identified using 3D/4D ultrasound
Proper location for placement of the embryos
- The middle of the endometrial cavity – half way from the internal os of the cervix to the uterine fundus (top of cavity) – is the best place.
- Care should be taken to keep the catheter between the top and bottom layers of the endometrium and not to allow it to dissect under the endometrial surface. (subendometrial embryo transfer) (success rates are lower)
Smooth, efficient and effective embryo transfer
Best with a full bladder for good ultrasound visualization and a better angle between cervix and uterus
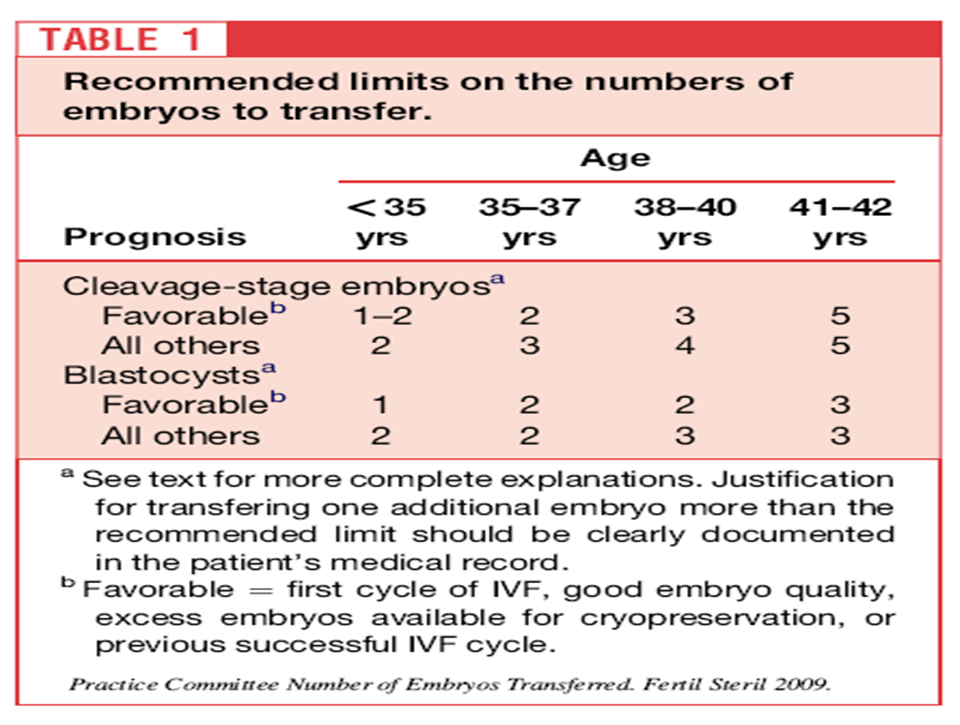
How Many Embryos are Transferred?
- Related to age and embryo quality
- –<35 = 2
- –35-37 = 2-3
- –38-40 = 3-4
- –>40 = up to 5
- –For patients with 2 or more failed IVF cycles, or a poor prognosis, can add more based on clinical judgement
Total embryo freezing
- Severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome
- Vaginal bleeding around the time of embryo transfer
- Thin endometrium (less than 5mm thickness) or polyps
- Unability to transfer the embryos fresh because of narrowing of the cervix
